Technology of carbon dioxide gas shielded welding pad

Most of the CO2 gas used for CO2 gas shielded welding is industrial by-product, which is compressed into liquid bottle for supply.
When the standard bottle is full at normal temperature, the pressure is 5-7mpa (50-70kgf / cm2). When it is lower than 1MPa (10 gauge pressures), it cannot be used continuously. The purity of CO2 gas for welding is more than 99% as specified in general technical standards. If the purity is found to be low during use, purification shall be carried out. When carbon dioxide gas shielded welding is used for low carbon steel and low alloy steel welding, in order to ensure the high mechanical properties of the weld and prevent the formation of pores, alloy steel welding wire with manganese, silicon and other deoxidizing elements must be used, and the carbon content in the welding wire should be limited. H08Mn2SiA is mainly used for welding of low carbon steel and low alloy steel; h04mn2sita has low carbon content and 0.2% - 0.4% titanium element, with strong anti porosity ability, and is used for welds with high requirements for compactness.
The specification parameters of CO2 gas shielded welding include power polarity, wire diameter, arc voltage, welding current, gas flow, welding speed, wire extension length, DC circuit inductance, etc.
(1) DC reverse connection shall be adopted when welding general materials with power polarity carbon dioxide gas shielded welding; DC positive connection shall be adopted when high-speed welding, surfacing and cast iron repair welding are carried out.
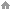
(2) The diameter of welding wire for CO2 gas shielded welding can generally be selected according to the table.
(3) Arc voltage and welding current for a certain diameter of welding wire, in CO2 gas shielded welding, the lower arc voltage is used, when the smaller welding current is used, the droplet formed by welding wire melting connects the base metal and welding wire, which is called short circuit state. Most CO2 gas shielded welding processes use short-circuit transfer welding. When the arc voltage is high and the welding current is high, the droplet flying off is called particle transition. This kind of transition is often used when the welding wire of φ 1.6 or φ 2.0mm is used to weld the plate automatically. Welding wire with diameter of over 3mm is seldom used. The short circuit transition is mainly used for the welding wire of Φ o.6 ~ φ 1.2mm. With the increase of the diameter of the welding wire, the number of splashing particles increases correspondingly. When φ 1.6mm welding wire is used and the short circuit transition is still maintained, the spatter will be very serious.

Welding current and arc voltage are key process parameters. In order to make the weld well formed, reduce the spatter and reduce the welding defects, the arc voltage and welding current should match each other, and adjust the welding current by changing the wire feeding speed. See the table for the typical process parameters and the range of process parameters used in production with the minimum spatter
In low current welding, if the arc voltage is too high, the metal spatter will increase; if the arc voltage is too low, the welding wire is easy to reach into the molten pool and make the arc unstable. In high current welding, if the arc voltage is too large, the metal spatter will increase, which is easy to produce air holes; if the voltage is too low, the arc will be too short, which will lead to poor weld formation.
(4) Gas flow
The flow rate of carbon dioxide is related to welding current, welding speed, extension length of welding wire and nozzle diameter. The gas flow rate should increase with the increase of welding current, welding speed and extension length of welding wire. Generally, the flow rate of carbon dioxide is 8-25l / min. If the flow rate of carbon dioxide is too large, due to the oxidation of the gas at high temperature, it will aggravate the burning loss of alloy elements, weaken the deoxidization and reduction of silicon and manganese elements, and more slag layers of silicon dioxide and manganese oxide will appear on the weld surface, making the weld prone to defects such as porosity; if the flow rate of carbon dioxide is too small, the stiffness of the gas flow layer is not strong, which will affect the weld pool and melting The protection effect of the drop is not good, and it is easy to produce defects such as porosity in the weld.
(5) Welding speed
With the increase of welding speed, the width, reinforcement and penetration of the weld decrease correspondingly. If the welding speed is too fast, the protective effect of gas will be damaged, and the cooling speed of the weld will be accelerated, so the plasticity of the weld will be reduced, and the weld formation will be poor. On the contrary, if the welding speed is too slow, the width of the weld will increase obviously, the heat of the weld pool will be concentrated, and the defects such as burn through are easy to occur.
(6) Extension length of welding wire
It refers to the length of the welding wire extending out of the nozzle during welding. When the extension length of the welding wire increases, the resistance value of the welding wire increases and the melting speed of the welding wire is accelerated. When the extension length of the welding wire is too long, the welding wire will melt in sections due to overheating, resulting in unstable welding process, serious metal splashing, poor weld formation and weakening the protective effect of gas on the weld pool; otherwise, when the extension length of the welding wire is too short, the welding current will increase and shorten The distance between the nozzle and the weldment makes the nozzle overheat, causing the metal spatter to stick or block the nozzle, thus affecting the air flow. Generally, the extension length of welding wire is 8-14mm for fine wire CO2 gas shielded welding and 10-20mm for coarse wire CO2 gas shielded welding.
(7) DC loop inductance
In the welding circuit, in order to make the welding arc stable and reduce spatter, it is generally necessary to connect appropriate inductors in series. When the inductance value is too large, the growth rate of short-circuit current is too slow, which will cause the metal splash of large particles and the explosion of welding wire in sections, resulting in arc extinguishing or making arc starting difficult; when the inductance value is too small, the growth rate of short-circuit current is too fast, which will cause the metal splash of very fine particles, make the weld edge uneven and poor forming. Moreover, the wound welding cable is equivalent to an additional inductance, so once the welding process is stable, do not change it casually. The operation technology of semi-automatic CO2 gas shielded welding is similar to that of electrode arc welding, and it is easier to master than electrode arc welding.
The operation process of semi-automatic CO2 gas shielded welding should pay attention to the following problems:
1. Due to the low no-load voltage of the flat external characteristic power supply and the smooth welding wire, the stable burning point of the arc is not easy to establish and the welding wire is easy to produce spatter during arc striking. Because of the low initial welding temperature of the workpiece, defects are easy to appear at the arc striking position. Generally, the short-circuit arc striking method is adopted; before arc striking, the welding wire end shall be cut off, because the spherical end formed by melting will cause splashing when arc striking again; during arc striking, the position shall be selected and the backward arc striking method shall be adopted.
2. It is easy to produce cracks and pores in the crater due to too fast arc stopping. The operation of arc stopping is more strict than that of electrode arc welding. Stop at the weld crater for a while, then slowly lift up the welding handle, and make the first layer of weld overlap 20-50mm at the joint.
3. For butt flat welding and transverse welding, the welding handle shall be slightly inclined, and the groove can be seen clearly with the left welding method, which is not easy to deviate. Both the left and right welding methods can be used in fillet welding.
4. Vertical and overhead welding. There are two welding methods for vertical welding, one is from top to bottom, which is fast, easy to operate, and the weld is flat and beautiful; however, the penetration is small and the joint strength is poor, so it is suitable for the weld without strength requirements. On the other hand, the weld is welded from the bottom to the top, the weld penetration is large, the reinforcement surface is high, but the shape is rough. The overhead welding should adopt fine welding wire, small current, low voltage and short circuit transition to maintain the stability of the welding process; the flow rate of CO2 gas should be slightly larger than that of the flat and vertical welding; when the temperature of the weld pool rises and the molten iron has a downward flow trend, the welding handle can swing back and forth to ensure the flatness of the weld shape.